Comprehensive Guide to Sinus Infection and Hearing Loss: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are a common health issue that affects millions of people each year. In some cases, sinus infections can lead to temporary or even permanent hearing loss. This comprehensive guide will explore the link between sinus infections and hearing loss, discussing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available. With over 2,000 words of detailed information, you'll gain a deep understanding of this important health topic.
What is a Sinus Infection?
A sinus infection, or sinusitis, occurs when the sinuses become inflamed and swollen due to a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection. The sinuses are hollow cavities within the skull that are lined with a thin layer of mucus-producing tissue. Their primary function is to produce mucus that helps to filter, warm, and moisten the air we breathe. When the sinuses become blocked or inflamed, mucus cannot drain properly, leading to a buildup of pressure and infection.
The Anatomy of the Ear and Sinuses
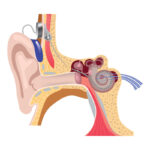
To understand the connection between sinus infections and hearing loss, it's important to know the basic anatomy of the ear and sinuses. The ear is divided into three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The Eustachian tubes are small, narrow tubes that connect the middle ear to the back of the throat and help equalize air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
The sinuses, on the other hand, are a series of interconnected air-filled cavities located within the skull. There are four pairs of sinuses: the maxillary sinuses, the frontal sinuses, the ethmoid sinuses, and the sphenoid sinuses. Each of these sinuses is lined with a mucous membrane that produces mucus to help filter, warm, and moisten the air we breathe.
How Sinus Infections Can Cause Hearing Loss
When a sinus infection occurs, the inflammation and swelling can block the Eustachian tubes, preventing them from equalizing air pressure in the middle ear. This can cause a buildup of fluid and pressure in the middle ear, leading to a condition called otitis media, or middle ear infection. Otitis media can cause temporary hearing loss due to the fluid and pressure interfering with the proper functioning of the eardrum and the tiny bones in the middle ear that transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear.
In some cases, a severe or long-lasting sinus infection can lead to permanent hearing loss. This can occur if the infection spreads to the inner ear, damaging the delicate structures responsible for hearing, or if the pressure and inflammation cause damage to the eardrum or the bones in the middle ear.
Symptoms of Sinus Infection-Related Hearing Loss
The symptoms of sinus infection-related hearing loss can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the extent of the hearing loss. Common symptoms include:
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with a sinus infection may also experience:
- Nasal congestion and discharge
- Facial pain or pressure
- Headache
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Bad breath
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you suspect that you have a sinus infection and are experiencing hearing loss, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional. A thorough examination, including a review of your medical history, a physical examination, and possibly imaging tests (such as X-rays or CT scans), can help determine the cause of your symptoms and the appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment for sinus infection-related hearing loss will typically involve addressing the underlying sinus infection first. This may include:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Nasal corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Antihistamines or decongestants for allergies or colds
- Saline nasal sprays or irrigation to help clear congestion
- Pain relievers and fever reducers
If the hearing loss is caused by a buildup of fluid in the middle ear, your healthcare provider may recommend additional treatments, such as:
- Oral or nasal steroids to reduce inflammation and promote drainage
- Antibiotic ear drops for middle ear infections
- Over-the-counter or prescription ear drops to help relieve pain and inflammation
- In severe cases, a procedure called a myringotomy, in which a small incision is made in the eardrum to allow fluid to drain
Prevention Tips
To reduce your risk of developing sinus infections and related hearing loss, consider the following tips:
- Practice good hand hygiene to avoid the spread of germs
- Keep your immune system strong by eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and getting enough sleep
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Maintain proper humidity levels in your home to prevent dryness and irritation of the nasal passages
- Use a saline nasal spray or irrigate your sinuses with a saline solution regularly to help keep your sinuses clear and healthy
When to Seek Medical Help
If you're experiencing symptoms of a sinus infection, including hearing loss, it's important to seek medical help as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications, such as permanent hearing loss. You should contact a healthcare professional if:
- Your symptoms persist for more than 10 days
- You have a high fever
- Your symptoms worsen after initially improving
- You have severe facial pain or headache
- You experience sudden or severe hearing loss
Conclusion
Sinus infections can be a painful and uncomfortable experience, and in some cases, they can lead to temporary or even permanent hearing loss. Understanding the connection between sinus infections and hearing loss, as well as the symptoms and treatment options, can help you take the necessary steps to protect your hearing and overall health. If you suspect that you have a sinus infection and are experiencing hearing loss, consult with a healthcare professional to receive the appropriate care.
Sources
- American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. (2021). Sinusitis. Retrieved from https://www.entnet.org/content/sinusitis
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Ear infection (middle ear). Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ear-infections/symptoms-causes/syc-20351616