Vitamin D & Tinnitus: Unraveling the Connection for Better Hearing Health
Are you suffering from tinnitus, that annoying ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in your ears? You're not alone. Millions of people around the world experience tinnitus, and many are on the lookout for effective treatment options. An often-overlooked factor that might be contributing to your tinnitus is a deficiency in vitamin D. In this in-depth, 2000-word blog post, we will explore the connection between vitamin D and tinnitus, discuss the importance of vitamin D for overall hearing health, and provide guidance on how to optimize your vitamin D levels for better hearing.
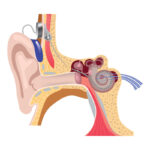
Understanding Tinnitus: Causes and Symptoms
Tinnitus is a common hearing issue characterized by ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in one or both ears. These sounds can be continuous or intermittent and can vary in pitch and volume. Tinnitus can significantly impact one's quality of life, causing problems like difficulty concentrating, sleeping, or even enjoying daily activities.
Causes of tinnitus can include:
- Noise-induced hearing loss
- Age-related hearing loss
- Ear infections
- Head or neck injuries
- Medications
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- Cardiovascular diseases
Vitamin D: What Is It and Why Is It Important?

Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in maintaining the health of our bones, immune system, and various other bodily functions. It's unique among vitamins because our bodies can synthesize it when our skin is exposed to sunlight. There are two primary forms of vitamin D: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol).
Some of the key functions of vitamin D include:
- Regulating calcium and phosphorus absorption
- Promoting bone health and preventing osteoporosis
- Strengthening the immune system
- Supporting cardiovascular health
- Enhancing mood and cognitive function
The Connection Between Vitamin D and Tinnitus
Recent research has found a possible link between vitamin D deficiency and tinnitus. Studies suggest that insufficient levels of vitamin D may contribute to the development or worsening of tinnitus symptoms. The potential reasons for this connection include:
- Inflammation: Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory properties. A deficiency can lead to increased inflammation in the body, which may contribute to tinnitus symptoms.
- Blood flow: Vitamin D helps regulate blood flow. Poor blood circulation in the inner ear may lead to tinnitus or exacerbate existing symptoms.
- Cochlear hair cell health: Vitamin D is essential for the proper functioning of the hair cells in the inner ear, which are responsible for transmitting sound to the brain. A deficiency may impair the health of these cells and contribute to tinnitus.
How to Optimize Your Vitamin D Levels

To improve your hearing health and potentially alleviate tinnitus symptoms, it's essential to maintain optimal vitamin D levels. Here are some ways to increase your vitamin D intake:
- Sun exposure: Spend 10-30 minutes in the sun daily, depending on your skin type and location.
- Diet: Consume foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified dairy products, and mushrooms.
- Supplements: If you can't get enough vitamin D from sunlight and diet, consider taking a vitamin D supplement. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Other Lifestyle Changes to Manage Tinnitus
In addition to optimizing your vitamin D levels, there are other lifestyle changes that can help you manage tinnitus more effectively:
- Reduce exposure to loud noises: Wear earplugs or noise-canceling headphones when exposed to loud environments. Keep the volume on your devices at a safe level.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol consumption: Both caffeine and alcohol can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms for some individuals. Try reducing your intake to see if it helps.
- Manage stress: Stress can worsen tinnitus symptoms. Engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get regular exercise: Physical activity can improve blood flow, including circulation to the inner ear, which may help alleviate tinnitus symptoms.
- Seek professional help: If your tinnitus is severely affecting your quality of life, consult a hearing specialist for evaluation and potential treatment options.
Conclusion
While tinnitus can be a frustrating and challenging condition to live with, understanding the potential connection between vitamin D and tinnitus can provide new avenues for treatment and management. By optimizing your vitamin D levels and making other lifestyle changes, you may be able to improve your hearing health and reduce the impact of tinnitus on your daily life. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or supplementation routine.
Sources
- Bhatt, J. M., Lin, H. W., & Bhattacharyya, N. (2016). Prevalence, Severity, Exposures, and Treatment Patterns of Tinnitus in the United States. JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, 142(10), 959-965. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/article-abstract/2542617
- Kwon, Y. B., Jang, Y. S., & Han, K. (2021). Association between serum vitamin D levels and tinnitus in middle-aged adults: a cross-sectional study. The Laryngoscope, 131(4), E1334-E1340. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/lary.29132
- Holick, M. F. (2007). Vitamin D deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine, 357(3), 266-281. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra070553
- Nair, R., & Maseeh, A. (2012). Vitamin D: The “sunshine” vitamin. Journal of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics, 3(2), 118-126. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3356951/