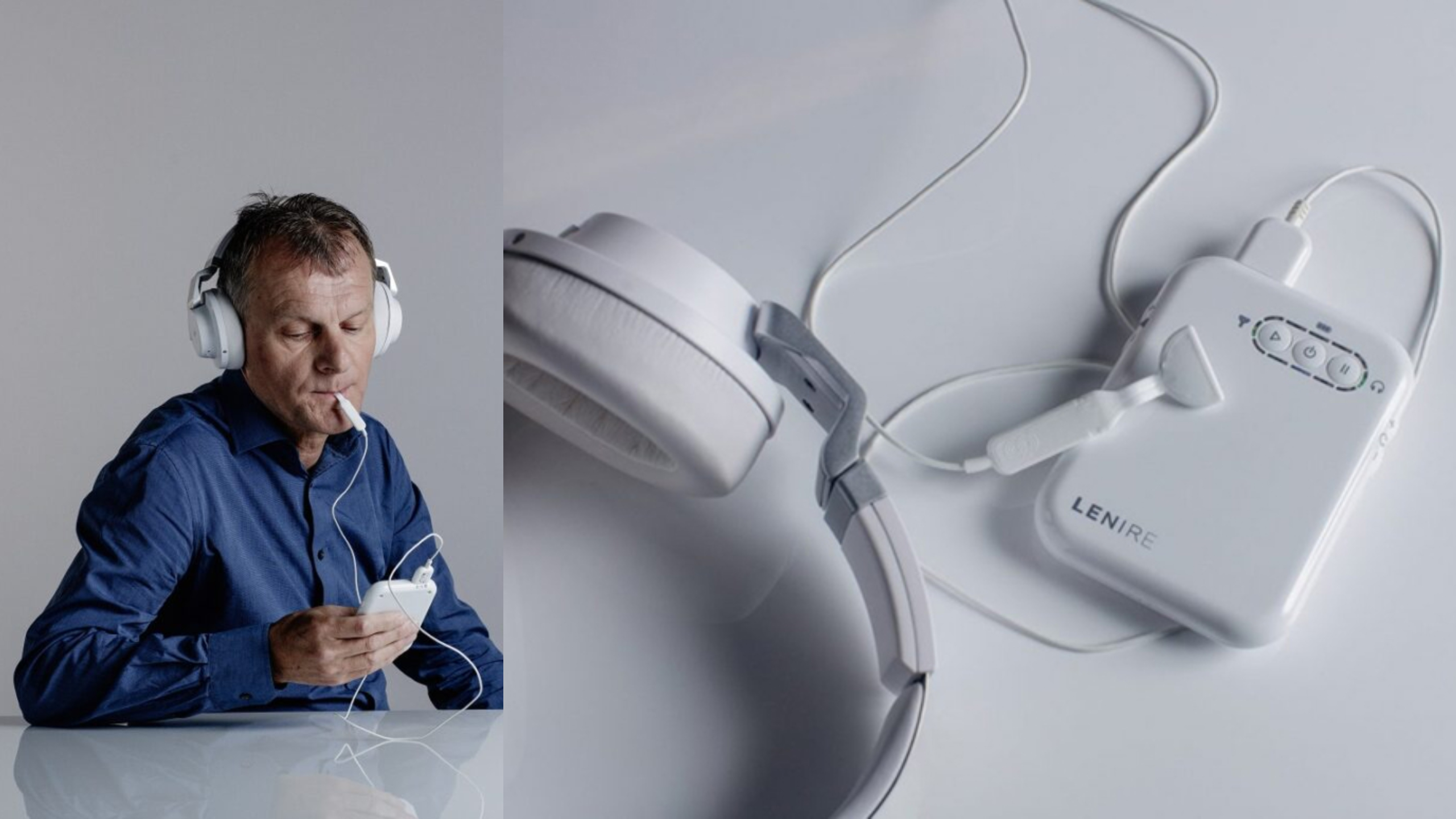
Neuromodulation and Tinnitus: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment and Management
Tinnitus, a ringing, buzzing, or hissing noise in the ears, affects millions of people worldwide. While some may consider it a minor annoyance, others experience severe discomfort, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Neuromodulation has emerged as a promising treatment option for tinnitus sufferers. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the science behind neuromodulation, its applications in tinnitus treatment, and the various techniques available. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each method, you'll be better equipped to make informed decisions about your tinnitus management plan.
Understanding Tinnitus: Causes and Symptoms
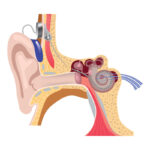
Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the ears or head without an external source, often described as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or clicking noises. This auditory sensation can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to loud noise, age-related hearing loss, ear infections, and certain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, and diuretics. In some cases, tinnitus may also be associated with medical conditions such as Meniere's disease, acoustic neuroma, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Symptoms of tinnitus can vary widely in severity, frequency, and duration, making the experience unique to each individual. Some people may experience constant noise, while others may notice intermittent episodes. The perceived volume of tinnitus can also fluctuate, ranging from subtle background noise to an overwhelming sound that interferes with daily activities and sleep.
Moreover, tinnitus can be categorized as either subjective, in which only the person experiencing the sound can hear it, or objective, where an external observer, such as a healthcare professional, can also detect the noise using specific instruments. Overall, tinnitus is a complex condition with various underlying causes and diverse manifestations, requiring personalized approaches to management and treatment.
What is Neuromodulation?
Neuromodulation is an innovative and advanced medical treatment that utilizes electrical or magnetic fields to modify the activity of targeted nerve cells or neural pathways within the nervous system.
This cutting-edge therapy has been employed to address a wide range of neurological and psychiatric conditions, including chronic pain, epilepsy, depression, and even movement disorders like Parkinson's disease.
The therapeutic potential of neuromodulation lies in its ability to modulate the function of specific brain regions or neural circuits, either by enhancing or inhibiting their activity, depending on the desired outcome.
In the context of tinnitus, neuromodulation aims to retrain the brain's neural circuits that are responsible for processing auditory information. Tinnitus is believed to be caused by abnormal neural activity in the central auditory system, which includes the auditory cortex and other brain areas involved in sound perception.
This aberrant activity is thought to be a maladaptive response to damage or dysfunction in the peripheral auditory system, such as the inner ear. By targeting and modulating the neural activity within these specific regions of the brain, neuromodulation has the potential to normalize the way the auditory system processes sound information, ultimately reducing or even eliminating the perception of the bothersome sounds associated with tinnitus.
The Science Behind Neuromodulation and Tinnitus
Tinnitus is thought to result from abnormal neural activity within the central auditory system, which includes the auditory cortex and other brain areas responsible for sound perception. This abnormal activity is believed to be a response to damage or dysfunction in the peripheral auditory system, such as the inner ear.
Neuromodulation techniques target these specific brain regions, aiming to modify their activity and normalize the way they process auditory information. By altering the neural circuits that generate tinnitus, neuromodulation may reduce or even eliminate the perception of the bothersome sounds.
Types of Neuromodulation Techniques for Tinnitus

There are several neuromodulation techniques that have been investigated for their potential to treat tinnitus. Each method has its unique advantages and challenges, making it crucial to understand their differences before choosing a treatment plan.
1. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
TMS uses magnetic fields to induce small electrical currents in targeted brain regions. This non-invasive technique has shown promise in reducing tinnitus severity and improving quality of life in some patients.
2. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
tDCS involves applying a weak electrical current to the scalp, which then penetrates the skull to stimulate specific brain areas. This non-invasive method has been found to improve tinnitus symptoms in some studies, though its effectiveness remains a topic of ongoing research.
3. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
VNS uses electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve, which runs from the brain stem to the abdomen, to modulate neural activity in the central auditory system. This invasive procedure requires the implantation of a device to deliver electrical pulses to the nerve. Some studies have shown VNS to be effective in reducing tinnitus symptoms when combined with auditory therapy.
4. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS is an invasive procedure that involves the implantation of electrodes within specific brain regions, such as the auditory cortex. These electrodes deliver electrical stimulation, modulating neural activity and potentially alleviating tinnitus symptoms. DBS has been primarily used for conditions like Parkinson's disease, but research into its potential for tinnitus treatment is still in its early stages.
Benefits and Risks of Neuromodulation for Tinnitus
The benefits of neuromodulation for tinnitus can include reduced severity and frequency of symptoms, improved quality of life, and better sleep. However, the effectiveness of these treatments can vary depending on the individual and the specific neuromodulation technique used. In some cases, neuromodulation may not provide significant relief from tinnitus symptoms.
The risks associated with neuromodulation depend on the specific technique employed. Non-invasive methods like TMS and tDCS generally have fewer risks and side effects, which may include mild discomfort, headache, or temporary changes in mood. Invasive techniques like VNS and DBS carry greater risks, such as infection, bleeding, and device malfunction. It is essential to discuss these risks with a healthcare professional before undergoing any neuromodulation procedure.
How to Choose the Right Neuromodulation Technique for You
Selecting the appropriate neuromodulation technique for your tinnitus depends on several factors, including the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, and your personal preferences. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an audiologist or neurologist, who can assess your condition and recommend the most suitable treatment options.
When considering neuromodulation for tinnitus, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and side effects. Non-invasive techniques like TMS and tDCS may be preferred for their lower risk profiles, but they may not be as effective for all individuals. Invasive procedures like VNS and DBS may offer more significant relief for some patients, but they come with increased risks and potential complications.
Conclusion
Neuromodulation is a promising treatment option for individuals suffering from tinnitus, offering the potential to alleviate bothersome symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the different neuromodulation techniques available and their respective benefits and risks, you can make an informed decision about which approach may be best suited for your needs. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential in determining the most appropriate treatment plan for your unique circumstances.
Sources
American Tinnitus Association. (n.d.). Tinnitus Treatments. https://www.ata.org/managing-your-tinnitus/treatment-options
Tyler, R., Cacace, A., Stocking, C., Tarver, B., Engineer, N., Martin, J., & Deshpande, A. (2017). Vagus nerve stimulation paired with tones for the treatment of tinnitus: a prospective randomized double-blind controlled pilot study in humans. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1-10. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-12178-w
Tunkel, D. E., Bauer, C. A., Sun, G. H., Rosenfeld, R. M., Chandrasekhar, S. S., & Cunningham, E. R. Jr (2014). Clinical practice guideline: tinnitus. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 151(2_suppl), S1-S40. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0194599814545325