Should You Take Tylenol to Treat Your Tinnitus? A Comprehensive Guide
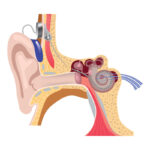
Tinnitus, a condition characterized by a constant ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no definitive cure, many tinnitus sufferers search for relief and treatment options to alleviate the bothersome symptoms.
One commonly debated remedy is the use of Tylenol, a popular over-the-counter pain reliever. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore whether Tylenol is an effective treatment option for tinnitus and delve into the science behind it.
Understanding Tinnitus: Causes and Symptoms

Before we delve into Tylenol's potential effects on tinnitus, it's important to understand the condition itself. Tinnitus is characterized by the perception of sound in the ears or head without an external source. It is a symptom rather than a standalone condition, often linked to underlying health issues such as:
- Age-related hearing loss
- Exposure to loud noise
- Earwax buildup
- Certain medications
- Ear or head injuries
- Stress and anxiety
- Cardiovascular problems
Tinnitus can manifest in different forms, such as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or clicking sounds, and can be temporary or chronic. The severity varies from person to person, ranging from mild to debilitating.
What is Tylenol and How Does It Work?
Tylenol, also known by its generic name acetaminophen, is a widely-used over-the-counter medication for pain relief and fever reduction. It is commonly used to treat headaches, menstrual cramps, toothaches, and minor aches and pains due to the common cold or flu.
Acetaminophen works by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that play a role in inflammation and pain sensation. It is a centrally acting analgesic, meaning it targets the central nervous system (CNS) to provide pain relief.
Tylenol and Tinnitus: Is There a Connection?
There is ongoing debate about the effectiveness of Tylenol in treating tinnitus. Some people claim that taking Tylenol alleviates their tinnitus symptoms, while others argue that it may exacerbate the problem.
It's important to note that Tylenol is not FDA-approved to treat tinnitus, nor is it marketed as a specific remedy for the condition. However, there is some anecdotal evidence and scientific research suggesting a possible connection between Tylenol and tinnitus.
The Science Behind Tylenol and Tinnitus

The scientific evidence on the effectiveness of Tylenol in treating tinnitus is limited and inconclusive. Some studies have shown that acetaminophen can provide short-term relief for tinnitus symptoms, particularly in cases where the condition is caused by inflammation or pain.
For instance, a study published in the American Journal of Otolaryngology in 2012 found that acetaminophen significantly reduced tinnitus symptoms in rats with noise-induced hearing loss. However, the study also noted that the improvement was temporary and further research was needed to determine its long-term effects.
On the other hand, some research suggests that high doses of acetaminophen may have ototoxic effects, meaning they could cause damage to the inner ear and potentially worsen tinnitus symptoms.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Using Tylenol for Tinnitus
While Tylenol is generally considered safe when used as directed, there are potential risks and side effects associated with its use, especially when taken in excessive amounts or for prolonged periods. Some potential side effects and risks include:
- Liver damage: Acetaminophen can be toxic to the liver when taken in high doses or over an extended period. This risk is exacerbated when combined with alcohol or other medications that also affect the liver.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to Tylenol, with symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Overuse of acetaminophen can cause stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Ototoxicity: As mentioned earlier, some research suggests that high doses of acetaminophen may cause damage to the inner ear, potentially worsening tinnitus symptoms.
Alternative Treatment Options for Tinnitus
If you're hesitant to use Tylenol for tinnitus relief or have found it ineffective, there are several alternative treatment options to consider. Some of these include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT is a form of therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It has been shown to help some individuals with tinnitus manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
- Sound therapy: Using white noise machines, hearing aids, or masking devices to introduce background noise can help some individuals with tinnitus by making the perceived sounds less noticeable.
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT): TRT combines sound therapy with counseling to help individuals habituate to their tinnitus and reduce the emotional impact of the condition.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs, may help alleviate tinnitus symptoms in some cases. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
- Lifestyle changes: Reducing stress, improving sleep habits, and managing underlying health conditions can all contribute to better tinnitus management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there is some anecdotal evidence and limited scientific research suggesting that Tylenol may provide temporary relief for tinnitus symptoms, it is not a definitive treatment option for the condition. Moreover, potential risks and side effects associated with acetaminophen use should be considered carefully. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before using Tylenol or any other medication for tinnitus treatment.
Alternative treatment options, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, sound therapy, and lifestyle changes, may provide more effective and long-term relief for individuals suffering from tinnitus. Ultimately, finding the most suitable treatment will depend on the individual's specific circumstances and the underlying cause of their tinnitus.
Sources
- Baguley, D., McFerran, D., & Hall, D. (2013). Tinnitus. The Lancet, 382(9904), 1600-1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60142-7
- Curhan, S. G., Eavey, R., Shargorodsky, J., & Curhan, G. C. (2010). Analgesic use and the risk of hearing loss in men. The American Journal of Medicine, 123(3), 231-237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.08.006