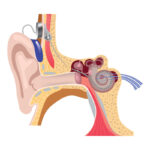
What Are the Symptoms of Tinnitus Sound? A Comprehensive Guide to Identifying and Managing This Common Auditory Condition
Tinnitus is a widespread auditory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various symptoms of tinnitus sound, its causes, and how it can be managed. This pillar content aims to provide you with a wealth of knowledge on tinnitus symptoms, enabling you to better understand this common condition and seek appropriate help when needed. With the use of best SEO practices, our goal is to rank high in search engines and reach a broad audience seeking information on tinnitus.
Understanding Tinnitus: Definition and Prevalence
Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the ears or head without an external source. These sounds can vary in pitch and intensity, ranging from a low hum to a high-pitched ringing. Tinnitus affects approximately 15-20% of the global population and can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life.
The Different Types of Tinnitus
There are two primary types of tinnitus: subjective and objective. Subjective tinnitus is the most common form and is experienced solely by the individual. Objective tinnitus, on the other hand, can be heard by both the person suffering from the condition and an external observer, such as a doctor. This type is less common and often has a specific underlying cause, such as vascular or muscular issues.
Common Symptoms of Tinnitus Sound
Tinnitus can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms can differ from one individual to another. Some of the most common tinnitus sounds include:
- Ringing
- Buzzing
- Hissing
- Whistling
- Humming
- Clicking
- Roaring
These sounds can be constant or intermittent and may vary in volume and pitch. Additionally, tinnitus can be experienced in one or both ears.
The Causes and Risk Factors of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Exposure to loud noise
- Age-related hearing loss
- Earwax buildup or blockage
- Ear or sinus infections
- Ototoxic medications
- Head or neck injuries
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- Meniere's disease
Risk factors for tinnitus include:
- Aging
- Prolonged exposure to loud noise
- Smoking
- Cardiovascular problems
- Stress and anxiety
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Tinnitus

To diagnose tinnitus, a healthcare professional will review your medical history and perform a physical examination, including an audiological evaluation. Additional tests may be conducted, such as imaging studies or blood tests, to identify the underlying cause of the condition.
Treatment for tinnitus depends on the specific cause and severity of the condition. Some possible treatment options include:
- Sound therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT)
- Medications, such as antidepressants or antianxiety drugs
- Hearing aids
- Cochlear implants or bone-anchored hearing aids
- Treating underlying conditions, such as earwax removal or managing TMJ disorders
How to Manage Tinnitus Symptoms at Home
In addition to seeking professional help, there are several strategies you can use to manage tinnitus symptoms at home:
- Use background noise: Introducing low-level background noise, such as white noise machines, fans, or soft music, can help mask tinnitus sounds and make them less noticeable.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and anxiety, which may exacerbate tinnitus symptoms.
- Limit exposure to loud noises: Protect your ears by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in noisy environments.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep can improve overall health and potentially reduce tinnitus symptoms.
- Avoid stimulants: Caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol may worsen tinnitus for some individuals, so consider limiting or avoiding these substances.
- Join a support group: Connecting with others who experience tinnitus can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Help
While tinnitus is often a benign condition, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
- Sudden onset of tinnitus without an apparent cause
- Tinnitus accompanied by dizziness, vertigo, or balance problems
- Tinnitus that affects your daily life, causing sleep disturbances, anxiety, or depression
- Tinnitus that coincides with hearing loss or ear pain
- Pulsatile tinnitus, a rhythmic sound in sync with your heartbeat
Conclusion
Tinnitus is a common auditory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors, you can better manage this condition and seek appropriate help when needed. Treatment options for tinnitus vary depending on the underlying cause, and several strategies can be employed at home to alleviate symptoms. Remember to consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your tinnitus or if it significantly impacts your quality of life.
Sources
- American Tinnitus Association. (n.d.). Understanding the Facts. Retrieved from https://www.ata.org/understanding-facts
- Mayo Clinic. (2021, August 10). Tinnitus. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tinnitus/symptoms-causes/syc-20350156
- National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). (2021, February 4). Tinnitus. Retrieved from https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/tinnitus
- British Tinnitus Association. (n.d.). Tinnitus. Retrieved from https://www.tinnitus.org.uk/tinnitus